Relative Clock¶
The Relative Clock executes single Steps in a specific timeline. It starts counting after signaling the first event. All subsequent events are relative to the preceding event.
| Relative Clock Steps |
|---|
| Define the Clock |
| Set Clock Properties |
| Signal an Event |
| Timed Step for Relative Clock |
| Example Test Case |
Define the Clock ¶
The following Step defines the Relative Clock.
Syntax
1 | <clock Variable> is a RelativeClock |
Parameter
- clock - The name assigned to the Relative Clock
Example
1 | And myClock is a RelativeClock |
Set Clock Properties ¶
This Step sets the Relative Clock's properties.
Syntax
1 | set clock.<event Identifier> to <number Number> |
Parameters
-
event - The name assigned to the Relative Clock's event
-
number - The numerical value of the event
Examples
1 2 | And set clock.initiateCall to 5 And set clock.answerCall to 10 |
Signal an Event ¶
After setting the properties, the Relative Clock must signal the event in order for it to take place.
Syntax
1 2 | clock signals <event Identifier>, <eventStep Step> |
Parameters
-
event - The name assigned to the Relative Clock's event
-
eventStep - The Step that follows the event
Example
1 2 | When clock signals initiateCall, A dials the number B.number When clock signals answerCall, B answers the incoming call |
Each event signaled by clock signals will be executed one after the other and relating to the one before. This means each time unit (except the first, which is relative to the first signal event Step) is relative to the previous Step.
Note: The test case will fail if a Step is not finished before the next event is signaled:
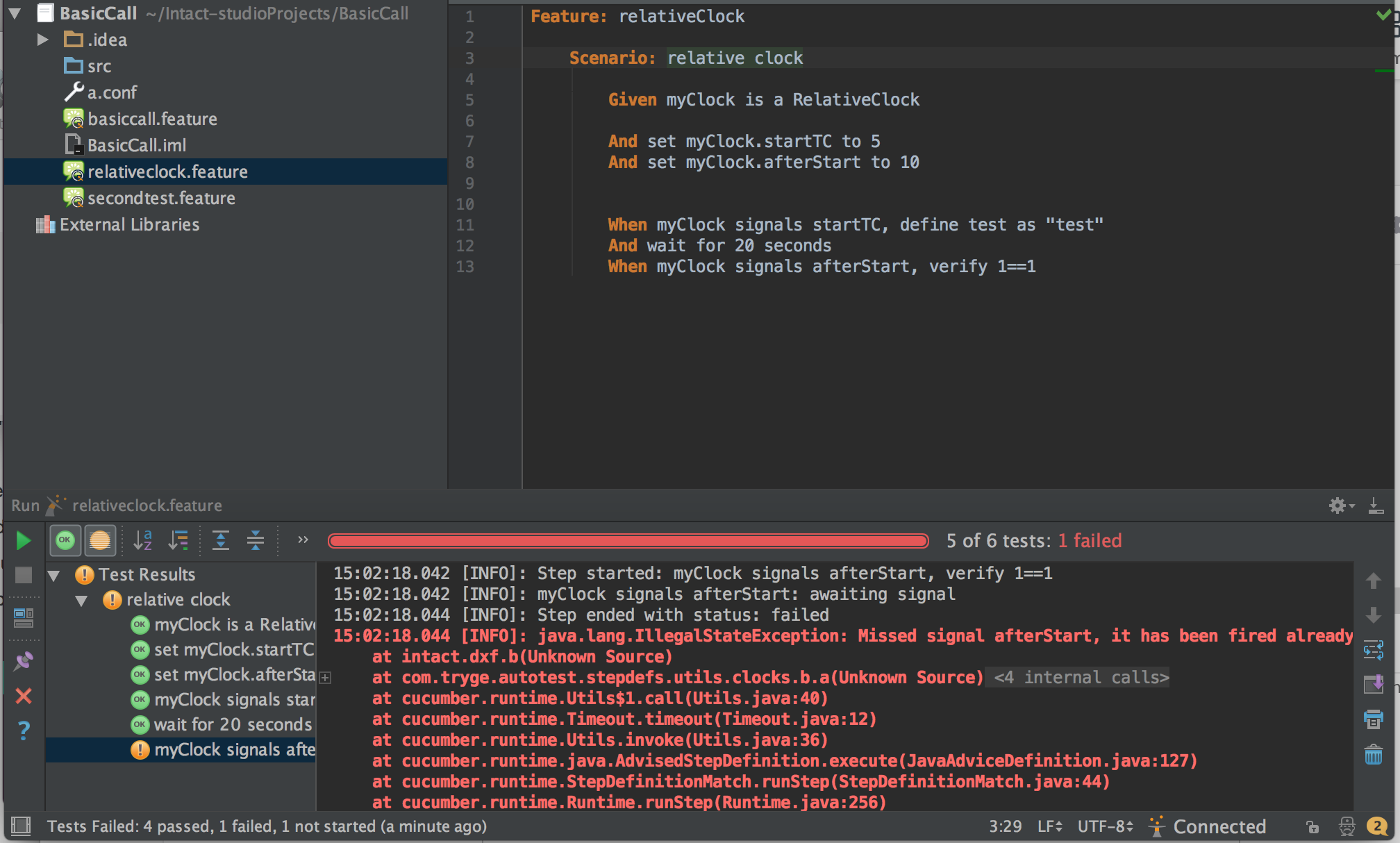
Timed Step for Relative Clock ¶
A timed Step can be included in the Relative Clock.
Syntax
1 | within <number Number> <time TimeUnits>, <eventStep Step> |
Parameters
-
number - The amount of time
-
time - Seconds or milliseconds
-
eventStep - The Step that follows the event
Example
1 2 3 4 | When clock signals initiateCall, A dials the number B.number And within 22 seconds, B detects an incoming call from A.number When clock signals answerCall, B answers the incoming call And within 1000 milliseconds, A connects |
Test Case Example ¶
3-Party Conference Call with Relative Clock Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | Feature: Conference Call Scenario Outline: Conference Call Given an Android phone as A And an Android phone as B And an Android phone as C And A sends the following ussd "*100#" And within 20 seconds, A receives an ussd response as RESP1 And extract data1 with ussdFirstAccEnq from RESP1.text And clock is a RelativeClock And set clock.initiateCall to <initC> And set clock.answerCall to <ansC> And set clock.initiateCon to <initCon> And set clock.answerCon to <ansCon> And set clock.releaseCon to <relCon> When clock signals initiateCall, A dials the number B.number And within 22 seconds, B detects an incoming call from A.number When clock signals answerCall, B answers the incoming call And within 10 seconds, A connects And after 3 seconds, A holds the call When clock signals initiateCon, A dials the number C.number And within 20 seconds, C detects an incoming call from A.number When clock signals answerCon, C answers the incoming call And after 5 seconds, A makes a conference call When clock signals releaseCon, A ends the call and, within 25 seconds, he and B disconnect And within 20 seconds, C disconnects Then verify !C.isConnected() And verify !B.isConnected() And verify !A.isConnected() And A sends the following ussd "*100#" And within 20 seconds, A receives an ussd response as RESP2 And extract data2 with ussdFirstAccEnq from RESP2.text Then the charge for <charge1>(<dur1>) + <charge2>(<dur2>) is (data1.bal - data2.bal) Examples: | initC | ansC | initCon | ansCon | relCon | dur1 | dur2 | charge1 | charge2 | | 5 | 25 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 60 | 25 | D2_001 | D2_001 | | 10 | 20 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 55 | 30 | D2_002 | D2_002 | |